| Appendix C. Annex: glossary | ||
|---|---|---|
 |  | |
Table of Contents
The relative deviation of a given region (i) to a context is defined by equation Figure C.1. The relative deviation depends on the chosen context (general, medium or local), it shows the gap between the value of the unit and the average value of the context. The deviation is expressed in a percentage of the context average value (100 is the pivot).
Figure C.1. Mathematical formula of the relative deviation
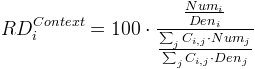
This figure shows a general formula to compute the relative deviation RD of a territorial unit i for the chosen context Context. Needed variables are:
Numx is the value of the indicator chosen as the Numerator parameter for the territorial unit x.
Denx is the value of the indicator chosen as the Denominator parameter for the territorial unit x.
Cij is a boolean whose value depends on the chosen context:
General context: Cij=1 if the current
territorial unit j is included in the reference area, Cij=0 in other cases.
For example, if the reference area is EU-15, Cij takes the value 1 for regions of EU-15 and the value 0 for regions of the candidate countries.
Territorial context: Cij shows if two regions i
and j belong or not to the same area. In the case when the medium context considers the state level,
Cij takes the value 1 for regions belonging to the same
state and the value 0 for regions belonging to different states.
Spatial context: Cij
shows the potential level of local interactions between two regions i and j. The local
interaction may be for example defined by a boolean variable which takes the value 1 for contiguous regions and the value 0 for
non-contiguous regions. Currently, we have decided that a region is not neighbour to itself (Locii=0) but
it is possible to choose the solution where a region is part of its own neighbourhood (Locii=1). Many alternative
solutions are possible according to the definition of the neighbourhood criterion (kilometres time, cost, length
of common boundary, ...) and to the measure of the potential level of interaction. This parameter may not be a boolean but
a continuous probabilistic function between 0 and 1.
See Also General deviation, Spatial deviation, Territorial deviation.
The set of elementary units compose (cover) the whole area, and constitute the elementary zoning.
See Also Elementary zoning.
Smallest division of the studied area. Each unit of this zoning is called elementary unit.
See Also Elementary unit.
Deviation when the context of reference is the general area. The reference can be an available study area or a any value chosen by the user.
See Also Deviation.
Deviation when the context of an unit is defined by the set of units that belongs to its neighbourhood (for instance adjacent units), contiguous regions by default.
See Also Deviation.
Deviation when the context is defined by a territorial unit that belongs to a chosen higher zoning level which contains the considered unit.
See Also Deviation.
Established by EUROSTAT for over 30 years, NUTS is a territorial subdivision system used in Europe "in order to provide a single uniform breakdown of territorial units for the production of regional statistics in the European Union" [1]. The NUTS zoning nomenclature for Europe organizes all units in a hierarchy of levels:
NUTS 0 groups administrative units at country level : France, Germany, Spain, Italy, etc.
NUTS 1 groups administrative units at great region level : ILE DE FRANCE, BASSIN PARISIEN, EST, CENTRE-EST, etc.
NUTS 2 groups administrative units at region level (Région in France - Länder in Germany - Comunidades autonomas in Spain, regioni in Italy) : ILE DE FRANCE, RHONE-ALPES, PACA, etc.
NUTS 3 groups administrative units at departement level (Département in France - Kreise in Germany - Provincias in Spain, Provincie in Italy): Essone, Isère, Savoie, etc.
NUTS 4 and NUTS 5 are now deprecated levels that are respectively replaced by LAU 1 and LAU 2.
LAU acronym stands for Local Administrative Unit.
HTML document that lists the set of parameters used for analysis (study area, zoning, context for deviation, indicators for numerator and denominator) and the maps which are generated by the application.
Social-economic count, like number of deaths on 1999 year, number of births on 1999 year, total population in thousand on 1999 year. Stocks should be valued on each elementary unit. There are also called indicators.
Territorial space on which we will base the analysis. It can be Europe, Cameroun, or France by example. Only one study area can be loaded in the same time by the application.
A ratio between two stocks which are defined and available on the same set of territorial units.
Context of analysis and selected options in the application when working on a study area: zoom level, map mode, etc. It can be exported to an XML file.